As Dominy Law Firm attorney Bryan Hawkins was preparing to litigate this issue in Franklin County, Ohio, an appeals court settled it. The issue is whether, in a DUI case (called ‘OVI’ in Ohio), a law enforcement officer can obtain the medical records of a suspect with a subpoena and without a search warrant. In the case of State v. Rogers, the Tenth District Court of Appeals held law enforcement’s procurement of an OVI suspect’s medical records without a search warrant violates the suspect’s Fourth Amendment right to be free from unreasonable searches and seizures.
As Dominy Law Firm attorney Bryan Hawkins was preparing to litigate this issue in Franklin County, Ohio, an appeals court settled it. The issue is whether, in a DUI case (called ‘OVI’ in Ohio), a law enforcement officer can obtain the medical records of a suspect with a subpoena and without a search warrant. In the case of State v. Rogers, the Tenth District Court of Appeals held law enforcement’s procurement of an OVI suspect’s medical records without a search warrant violates the suspect’s Fourth Amendment right to be free from unreasonable searches and seizures.
Articles Tagged with Search Warrant
Ohio Court Interprets Recent Supreme Court Decision For DUI/OVI Cases
 Over the past couple of years, this blog has followed and discussed the United States Supreme Court’s decision in Mitchell v. Wisconsion. While Supreme Court decisions can seem like seismic shifts in the law when they are issued, the reality is it often takes time for their effects to be felt on a practical level. Such is the case with Mitchell. While it was decided over a year-and-a-half ago, it is just now being discussed by Ohio Appellate Courts.
Over the past couple of years, this blog has followed and discussed the United States Supreme Court’s decision in Mitchell v. Wisconsion. While Supreme Court decisions can seem like seismic shifts in the law when they are issued, the reality is it often takes time for their effects to be felt on a practical level. Such is the case with Mitchell. While it was decided over a year-and-a-half ago, it is just now being discussed by Ohio Appellate Courts.
U.S. Supreme Court Delivers Disappointing DUI Decision
As discusse d previously in this space, we have been eagerly awaiting the Supreme Court’s decision in Mitchell v. Wisconsin. The Court set out to determine whether Wisconsin’s Implied Consent statute requires police to obtain a search warrant before getting a blood sample from an unconscious DUI suspect. The state of Wisconsin argued that Mitchell, through the state’s Implied Consent statute, had already consented to the blood draw, thereby removing the requirement for a warrant. Alternatively, they argued this should simply be viewed as an exercise of the State’s power to imposes conditions on a person’s privilege to operate a vehicle on Wisconsin’s roads.
d previously in this space, we have been eagerly awaiting the Supreme Court’s decision in Mitchell v. Wisconsin. The Court set out to determine whether Wisconsin’s Implied Consent statute requires police to obtain a search warrant before getting a blood sample from an unconscious DUI suspect. The state of Wisconsin argued that Mitchell, through the state’s Implied Consent statute, had already consented to the blood draw, thereby removing the requirement for a warrant. Alternatively, they argued this should simply be viewed as an exercise of the State’s power to imposes conditions on a person’s privilege to operate a vehicle on Wisconsin’s roads.
High Court Hears Oral Argument In Third Case Involving Warrantless Blood Test
 The United States Supreme Court recently heard oral arguments in the case of Mitchell v. Wisconsin. As this blog discussed previously, this the third case in a series of cases dealing with whether the police can take a DUI/OVI suspect’s blood without a search warrant. The questions and statements from the bench during the oral argument may telegraph how each justice views the issue. However, in our experience, it is difficult to predict the outcome of a case based on the oral arguments.
The United States Supreme Court recently heard oral arguments in the case of Mitchell v. Wisconsin. As this blog discussed previously, this the third case in a series of cases dealing with whether the police can take a DUI/OVI suspect’s blood without a search warrant. The questions and statements from the bench during the oral argument may telegraph how each justice views the issue. However, in our experience, it is difficult to predict the outcome of a case based on the oral arguments.
Officer Obtains Urine Test Result From Nurse: DUI Dismissed
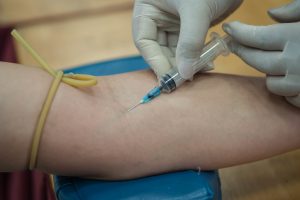 Brynn Campbell was involved in a head on-crash which killed the 83-year-old woman driving the other car. Campbell was taken to the hospital, and hospital staff performed a urine test. Although Campbell showed no obvious signs of impairment, a police officer went to the hospital and asked the nurse for the urine test results. The results showed Campbell’s alcohol level was well over the limit, according to the Global News. The officer then obtained a search warrant to obtain Campbell’s urine samples and have them tested. Campbell was charged with vehicular homicide. She was acquitted by the trial court, and the prosecution appealed.
Brynn Campbell was involved in a head on-crash which killed the 83-year-old woman driving the other car. Campbell was taken to the hospital, and hospital staff performed a urine test. Although Campbell showed no obvious signs of impairment, a police officer went to the hospital and asked the nurse for the urine test results. The results showed Campbell’s alcohol level was well over the limit, according to the Global News. The officer then obtained a search warrant to obtain Campbell’s urine samples and have them tested. Campbell was charged with vehicular homicide. She was acquitted by the trial court, and the prosecution appealed.
Preview: Third Episode In Trilogy Addressing Blood Tests And Search Warrants
 Just as Hollywood has produced some good movies in trilogies, the United States Supreme Court has produced some good case law in trilogies. The Court addressed the right to confront crime lab analysts with the trinity of Bullcoming, Melendez-Diaz and Williams. On the issue of the need for a warrant to draw blood from a DUI suspect, two-thirds of the triad have been completed: McNeely and Birchfield. The triumvirate is about to be consummated with Mitchell v. Wisconsin.
Just as Hollywood has produced some good movies in trilogies, the United States Supreme Court has produced some good case law in trilogies. The Court addressed the right to confront crime lab analysts with the trinity of Bullcoming, Melendez-Diaz and Williams. On the issue of the need for a warrant to draw blood from a DUI suspect, two-thirds of the triad have been completed: McNeely and Birchfield. The triumvirate is about to be consummated with Mitchell v. Wisconsin.
U.S. Supreme Court Decides Constitutionality Of Warrantless Blood Tests And Breath Tests In DUI Cases
 Last week, the United States Supreme Court released a decision in a trio of cases involving DUI refusal laws. A previous article in this blog gives a preview of the cases. To decide the outcomes of those cases, the court analyzes whether search warrants are required before law enforcement officers can administer breath tests and blood tests. Based on that analysis, the Court decides whether states can make it illegal to refuse chemical tests in DUI cases. The Court’s decision will impact Ohio DUI/OVI cases.
Last week, the United States Supreme Court released a decision in a trio of cases involving DUI refusal laws. A previous article in this blog gives a preview of the cases. To decide the outcomes of those cases, the court analyzes whether search warrants are required before law enforcement officers can administer breath tests and blood tests. Based on that analysis, the Court decides whether states can make it illegal to refuse chemical tests in DUI cases. The Court’s decision will impact Ohio DUI/OVI cases.
 Columbus OVI/DUI Attorney Blog
Columbus OVI/DUI Attorney Blog